GROUP FLIEGER / Project FL 359/11-1
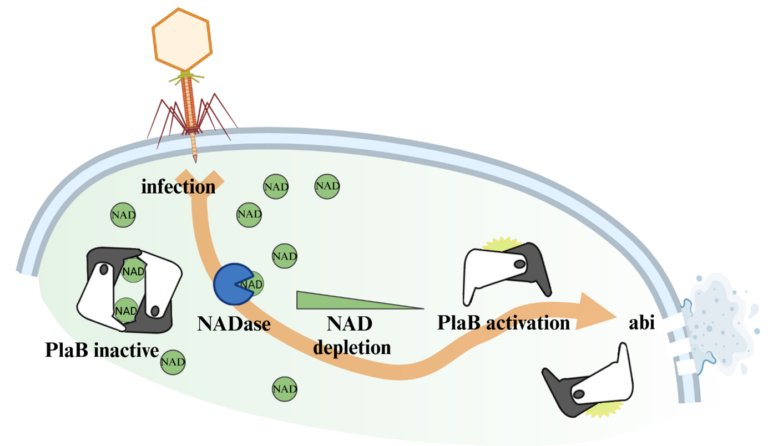
Like eukaryotes, bacteria possess a variety of mechanisms, such as NAD+ depletion, to counteract viral infections but many details of phage defense are currently not understood. We recently uncovered the unusual mechanism which controls activity of the bacterial virulence factor and phospholipase PlaB by NAD+. Specifically, physiological concentrations of NAD+ stabilize inactive PlaB tetramers while low NAD+ results in dissociation into active PlaB dimers and unleashment of fierce phospholipase activity. Since NAD+ is usually confined to the intracellular milieu, we presumed an intrinsic function of PlaB in programmed bacterial cell death which is key to abortive phage infection (abi). Now we aim to analyze PlaBs characteristics as a putative death effector and its interplay with NAD+ depletion in the context of phage infection.
Principal Investigator(s)

Prof. Dr. Antje Flieger
Robert Koch-Institut
Division of Enteropathogenic Bacteria and Legionella
National Reference Center for Salmonella and other Enteric Bacterial Pathogens
Consultant Laboratory for Listeria
E-Mail: fliegera@rki.de
Homepage: https://www.rki.de/EN/Content/Institute/DepartmentsUnits/InfectDiseases/Div11/Div11_node.html
PhD student(s)
Markosovo Marjaya: marjayam@rki.de
Publications
- Diwo M#, Michel W#, Aurass P, Kuhle-Keindorf K, Pippel J, Krausze J, Wamp S, Lang C, Blankenfeldt W*, and Flieger A* (2021) NAD(H)-mediated tetramerization controls the activity of Legionella pneumophila phospholipase PlaB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 */# equal contribution. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.201704611
- Hiller M#, Diwo M#, Wamp S, Gutsmann T, Lang C, Blankenfeldt W*, Flieger A* (2024) Structure-function relationships underpin disulfide loop cleavage-dependent activation of Legionella pneumophila lysophospholipase A PlaA. Mol Microbiol. 21(3):497-512. */# equal contribution. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.15201
- Neuber J, Lang C, Aurass P, Flieger A. (2024) Tools and mechanisms of vacuolar escape leading to host egress in Legionella pneumophila infection: Emphasis on bacterial phospholipases Mol Microbiol. 121(3):368-384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.15183
