GROUP VOGEL / Project VO 875/23-1
Molecular factors whereby giant phage ΦKZ modulates host protein synthesis
Phages with large genomes and complex lifestyles represent exciting opportunities to discover new molecular factors and principles of host manipulation during infection.
We use RNA and protein centric high-throughput techniques to map the transcriptome and proteome of phage ΦKZ and infected Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells for prediction of novel complexes involved in the process of usurping the host bacterium. For example, we have identified phage factors that directly target the host ribosome immediately after infection (Figure 1, Gerovac et al. 2023).
This project will provide important biological insight into the phage-host interface by identification and characterization of phage proteins that target host complexes with potential for exploitation in antimicrobial strategies and may yield new tools for synthetic biology.
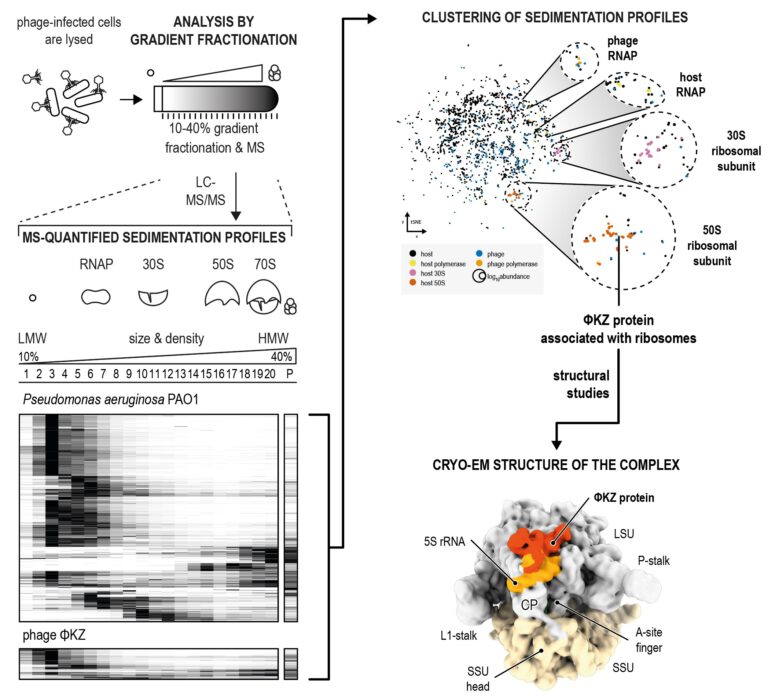
Figure 1: Grad-seq of phage infected cells. Complexes between proteins and RNAs from phage-infected cells are analysed by size in gradient fractionation. The proteins are identified and quantified by mass spectrometry and sedimentation profiles from host and phage proteomes are clustered. This results in phage factors that associate with the gene expression machinery. For example, a ΦKZ factor associated with 50S ribosomal proteins. We determined the cryo-EM structure of this factor on the 70S ribosome in interaction the 5S ribosomal RNA. (Gerovac et al. 2023)
Principal Investigator

Prof. Dr. Jörg Vogel
Institute for Molecular Infection Biology (IMIB) – University Würzburg
Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI)
E-Mail: joerg.vogel@uni-wuerzburg.de
Homepage: http://www.imib-wuerzburg.de/
https://www.helmholtz-hiri.de/
PhD student(s)
TBA
PostDocs
Dr. Milan Gerovac, milan.gerovac@uni-wuerzburg.de
Publications
- Gerovac M, Chihara K, Wicke L, Böttcher B, Lavigne R, Vogel J (2023)
Immediate targeting of host ribosomes by jumbo phage encoded proteins.
bioRxiv doi:10.1101/2023.02.26.530069. - Gerovac M, Wicke L, Chihara K, Schneider C, Lavigne R, Vogel J (2020)
A Grad-seq view of RNA and protein complexes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa under standard and bacteriophage predation conditions.
mBio 12(1):e03454-20, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.03454-20. - Wicke L, Ponath F, Coppens L, Gerovac M, Lavigne R, Vogel J (2020)
Introducing differential RNA-seq mapping to track the early infection phase for Pseudomonas phage ɸKZ.
RNA Biology 18(8):1099-1110, doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1827785.
